The internal organs consist of ;
1) the glands which produce essential substance. These are;
a. Two testes
b. Two seminal vesicles;
c. One prostate glands;
d. Two Cowper’s glands
2. The structures which act as passages for transportation of the secretions from the glands are made up of:
a. Two epididemis;
b. Two bad deferens ;
c. One urethra
The testes
There are two testes, one in separate compartment in the scrotum that protects them from injury
Function : Each testis contains small tubes where
sperm are reproduce from puberty
onwards.
The testes produce the male hormones called testosterone.
The spermatozoa : The sperm is about 0.05mm long and only visible under a microscope. It has a head, neck and fine long tail. Sperm are produce in the testicles from puberty onwards into old age. They take 3 months to mature. They travel at a very fast speed approximately 1 millimeter every second.
Function : They fertilize the female ripe egg released by the ovaries
The epididemis : These are two tubes located in the scrotum, tightly coiled and running down the back of testicles.
Function : They produce substance which stimulate the development of the sperm.
The Vas Deferens : These are the coiled ducts of the epidide
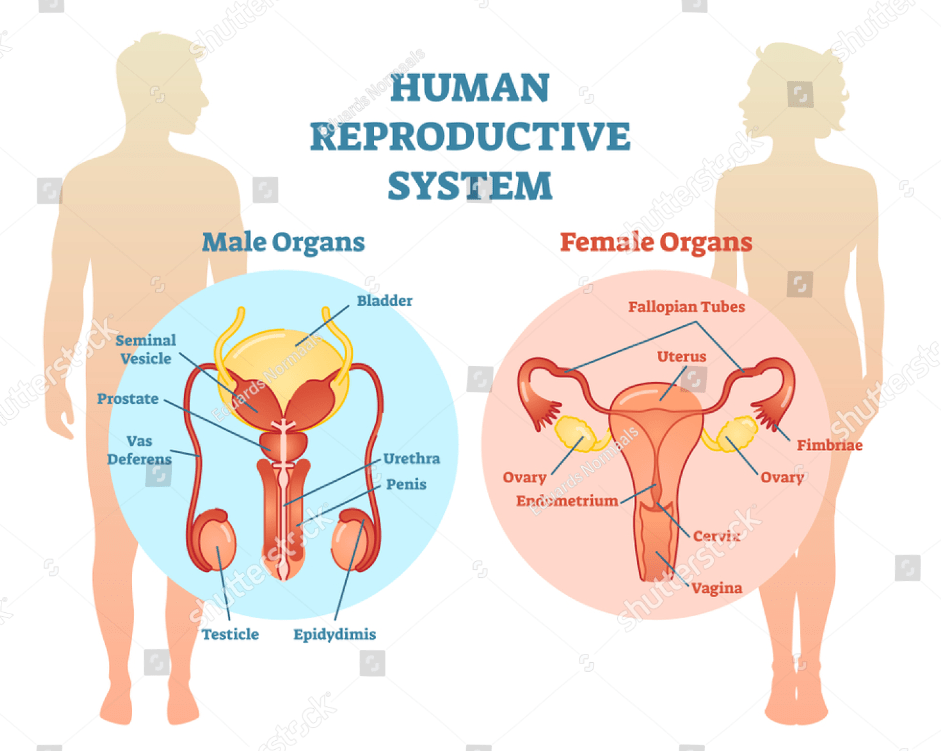
mis each leading into a tube. There are two of these tubes which are about 18 inches long and run from the scrotum into the pelvis.
Function : The tubes carry sperm from the epididemis to the seminal vesicles.
The Seminal vesicles : The two seminal vesicles are situated just below the bladder.
Function : They produce a sticky substance which is very important for the survival of the sperm that migrate into them from the testicles before ejaculation. The sticky substance contains nutrients for sperm survival as well as a medium that ensure sperm movement.
The prostate glands : It is located below the bladder and is made of glandular and muscular tissue.
Function :
1. It secrets an alkaline fluids which help the sperm to move.
2. It neutralize the acidity of the vaginal during the intercourse and that of the male urethra just before ejaculation so that the sperm do not die.
The Cowper’s glands : These are two small glands which join the urethra as it leaves the prostate.
Function : They secret lubricant fluids when an individual is sexually excited.
The urethra : This is the tube of about 8 inches long which travels from the bladder through the prostate beneath the pubic bone and through the whole length of the penis. During urination , the urine from the bladder flows through the urethra. And during sexual intercourse , the small muscle located at the opening of the bladder close up to allow the sperm mixed with semen to pass through it without being contaminated with urine.
Function : It serves as an outlet for urine and semen.
NOTE : The secretions of seminal versicles, prostate glands, and Cowper’s glands are known as semen or seminal fluid